Virtual Columns in Databend: Accelerating Queries on Semi-Structured Data
Virtual columns in Databend provide a powerful and automatic way to significantly accelerate queries on semi-structured data, particularly data stored in the Variant data type. This feature dynamically optimizes data access, leading to faster query execution and reduced resource consumption.
Overview
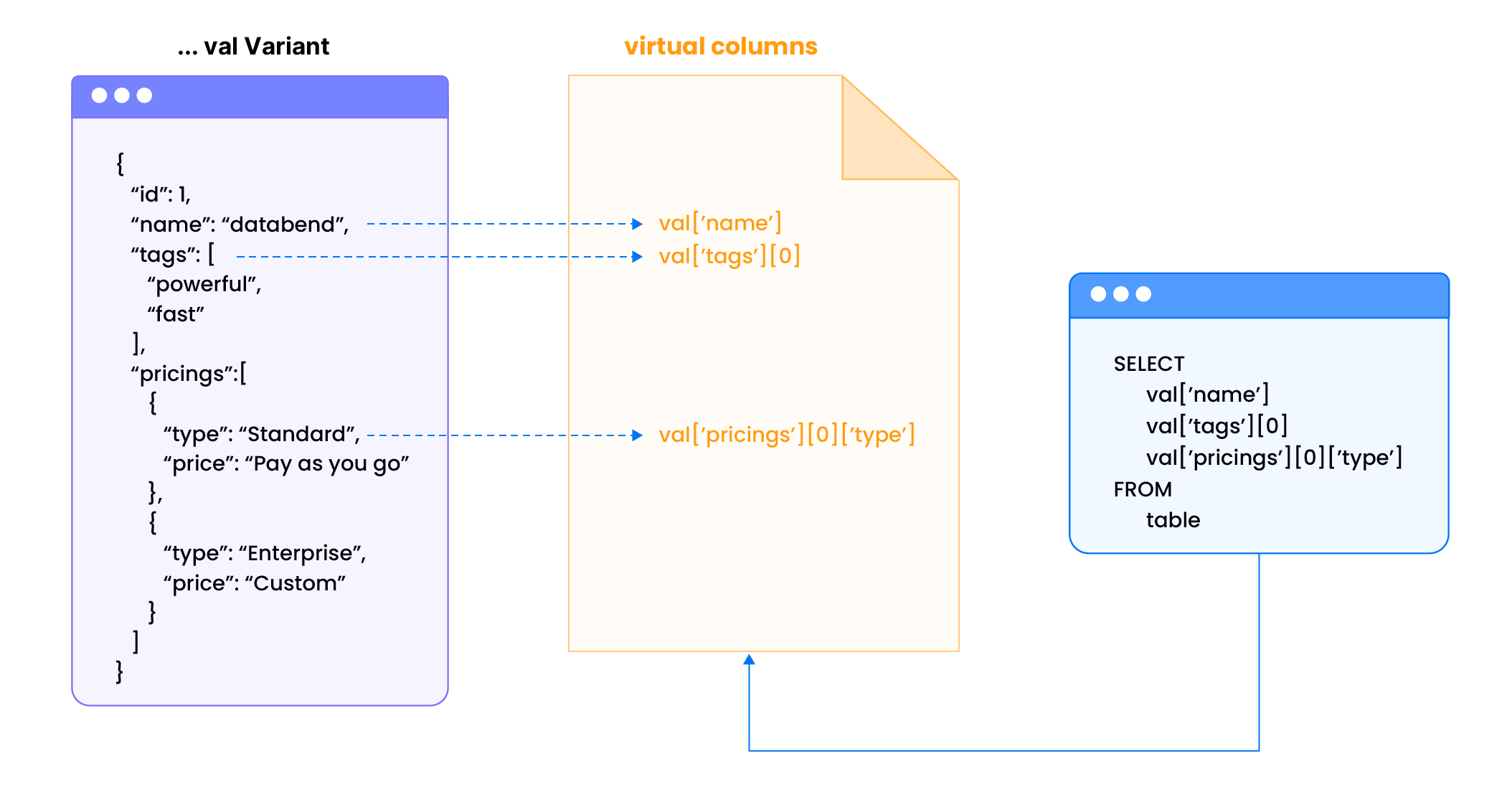
When working with nested data structures within VARIANT columns, accessing specific data points can be a performance bottleneck. Databend's virtual columns address this by automatically identifying and optimizing nested fields. Instead of repeatedly traversing the entire nested structure, virtual columns enable direct data retrieval, similar to accessing regular columns.
Databend automatically detects nested fields within VARIANT columns during data ingestion. If a field meets a certain threshold for presence, it's materialized as a virtual column in the background, ensuring that data is readily available for optimized querying. This process is entirely automatic, requiring no manual configuration or intervention.
Performance Benefits
- Significant Query Acceleration: Virtual columns dramatically reduce query execution time by enabling direct access to nested fields. This eliminates the overhead of traversing complex JSON structures for each query.
- Reduced Resource Consumption: By materializing only the necessary nested fields, virtual columns minimize memory consumption during query processing. This leads to more efficient resource utilization and improved overall system performance.
- Automatic Optimization: Databend automatically identifies and materializes fields as virtual columns. The query optimizer then automatically rewrites queries to utilize these virtual columns when accessing data within the
VARIANTcolumn. - Transparent Operation: The creation and management of virtual columns are entirely transparent to the user. Queries are automatically optimized without requiring any changes to the query syntax or data loading process. The query optimizer handles the rewriting of queries to leverage virtual columns.
How it Works
- Data Ingestion: When data containing
VARIANTcolumns is ingested, Databend analyzes the structure of the JSON data. - Field Presence Check: Databend checks if a nested field meets a certain threshold for presence.
- Virtual Column Materialization: If the field presence threshold is met, the system automatically materializes the field as a virtual column in the background.
- Query Optimization: When a query accesses a nested field within a
VARIANTcolumn, the query optimizer automatically rewrites the query to use the corresponding virtual column for faster data retrieval.
Important Considerations
- Overhead: While virtual columns generally improve query performance, they do introduce some storage and maintenance overhead. Databend automatically balances the benefits of virtual columns against this overhead to ensure optimal performance.
- Experimental Feature: Virtual columns are currently an experimental feature. They are disabled by default. To enable virtual columns, you must set the
enable_experimental_virtual_columnsetting to1: - Automatic Refresh: Virtual columns will be refreshed automatically after inserting data. If you don't want to generate virtual column data automatically, you can set
enable_refresh_virtual_column_after_writeto0to disable the generation of virtual columns. Asynchronous refresh can be done by using the refresh virtual column command. For details, see REFRESH VIRTUAL COLUMN. - Show Virtual columns: You can view information about virtual columns through the SHOW VIRTUAL COLUMNS command, and you can view information about virtual column metas through the FUSE_VIRTUAL_COLUMN system function.
Usage Examples
This example demonstrates the practical use of virtual columns and their impact on query execution:
SET enable_experimental_virtual_column=1;
-- Create a table named 'test' with columns 'id' and 'val' of type Variant.
CREATE TABLE test(id int, val variant);
-- Insert sample records into the 'test' table with Variant data.
INSERT INTO
test
VALUES
(
1,
'{"id":1,"name":"databend","tags":["powerful","fast"],"pricings":[{"type":"Standard","price":"Pay as you go"},{"type":"Enterprise","price":"Custom"}]}'
),
(
2,
'{"id":2,"name":"databricks","tags":["scalable","flexible"],"pricings":[{"type":"Free","price":"Trial"},{"type":"Premium","price":"Subscription"}]}'
),
(
3,
'{"id":3,"name":"snowflake","tags":["cloud-native","secure"],"pricings":[{"type":"Basic","price":"Pay per second"},{"type":"Enterprise","price":"Annual"}]}'
),
(
4,
'{"id":4,"name":"redshift","tags":["reliable","scalable"],"pricings":[{"type":"On-Demand","price":"Pay per usage"},{"type":"Reserved","price":"1 year contract"}]}'
),
(
5,
'{"id":5,"name":"bigquery","tags":["innovative","cost-efficient"],"pricings":[{"type":"Flat Rate","price":"Monthly"},{"type":"Flex","price":"Per query"}]}'
);
INSERT INTO test SELECT * FROM test;
INSERT INTO test SELECT * FROM test;
INSERT INTO test SELECT * FROM test;
INSERT INTO test SELECT * FROM test;
INSERT INTO test SELECT * FROM test;
-- Show the virtual columns
-- Explain the query execution plan for selecting specific fields from the table.
EXPLAIN
SELECT
val ['name'],
val ['tags'] [0],
val ['pricings'] [0] ['type']
FROM
test;
-[ EXPLAIN ]-----------------------------------
Exchange
├── output columns: [test.val['name'] (#3), test.val['pricings'][0]['type'] (#5), test.val['tags'][0] (#8)]
├── exchange type: Merge
└── TableScan
├── table: default.default.test
├── output columns: [val['name'] (#3), val['pricings'][0]['type'] (#5), val['tags'][0] (#8)]
├── read rows: 160
├── read size: 1.69 KiB
├── partitions total: 6
├── partitions scanned: 6
├── pruning stats: [segments: <range pruning: 6 to 6>, blocks: <range pruning: 6 to 6>]
├── push downs: [filters: [], limit: NONE]
├── virtual columns: [val['name'], val['pricings'][0]['type'], val['tags'][0]]
└── estimated rows: 160.00
-- Explain the query execution plan for selecting only the 'name' field from the table.
EXPLAIN
SELECT
val ['name']
FROM
test;
-[ EXPLAIN ]-----------------------------------
Exchange
├── output columns: [test.val['name'] (#2)]
├── exchange type: Merge
└── TableScan
├── table: default.book_db.test
├── output columns: [val['name'] (#2)]
├── read rows: 160
├── read size: < 1 KiB
├── partitions total: 16
├── partitions scanned: 16
├── pruning stats: [segments: <range pruning: 6 to 6>, blocks: <range pruning: 16 to 16>]
├── push downs: [filters: [], limit: NONE]
├── virtual columns: [val['name']]
└── estimated rows: 160.00
-- Display all the auto generated virtual columns.
SHOW VIRTUAL COLUMNS WHERE table='test';
╭────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ database │ table │ source_column │ virtual_column_id │ virtual_column_name │ virtual_column_type │
│ String │ String │ String │ UInt32 │ String │ String │
├──────────┼────────┼───────────────┼───────────────────┼──────────────────────────┼─────────────────────┤
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000000 │ ['id'] │ UInt64 │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000001 │ ['name'] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000002 │ ['pricings'][0]['price'] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000003 │ ['pricings'][0]['type'] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000004 │ ['pricings'][1]['price'] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000005 │ ['pricings'][1]['type'] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000006 │ ['tags'][0] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000007 │ ['tags'][1] │ String │
╰────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯