COPY INTO <table>
COPY INTO allows you to load data from files located in one of the following locations:
- User / Internal / External stages: See What is Stage? to learn about stages in Databend.
- Buckets or containers created in a storage service.
- Remote servers from where you can access the files by their URL (starting with "https://...").
- IPFS and Hugging Face repositories.
See also: COPY INTO <location>
Syntax
/* Standard data load */
COPY INTO [<database_name>.]<table_name> [ ( <col_name> [ , <col_name> ... ] ) ]
FROM { userStage | internalStage | externalStage | externalLocation }
[ FILES = ( '<file_name>' [ , '<file_name>' ] [ , ... ] ) ]
[ PATTERN = '<regex_pattern>' ]
[ FILE_FORMAT = (
FORMAT_NAME = '<your-custom-format>'
| TYPE = { CSV | TSV | NDJSON | PARQUET | ORC | AVRO } [ formatTypeOptions ]
) ]
[ copyOptions ]
/* Data load with transformation */
COPY INTO [<database_name>.]<table_name> [ ( <col_name> [ , <col_name> ... ] ) ]
FROM (
SELECT {
[<alias>.]<column> [, [<alias>.]<column> ...] -- Query columns by name
| [<alias>.]$<col_position> [, [<alias>.]$<col_position> ...] -- Query columns by position
| [<alias>.]$1[:<column>] [, [<alias>.]$1[:<column>] ...] -- Query rows as Variants
} ]
FROM {@<stage_name>[/<path>] | '<uri>'}
)
[ FILES = ( '<file_name>' [ , '<file_name>' ] [ , ... ] ) ]
[ PATTERN = '<regex_pattern>' ]
[ FILE_FORMAT = (
FORMAT_NAME = '<your-custom-format>'
| TYPE = { CSV | TSV | NDJSON | PARQUET | ORC | AVRO } [ formatTypeOptions ]
) ]
[ copyOptions ]
Where:
userStage ::= @~[/<path>]
internalStage ::= @<internal_stage_name>[/<path>]
externalStage ::= @<external_stage_name>[/<path>]
externalLocation ::=
/* Amazon S3-like Storage */
's3://<bucket>[/<path>]'
CONNECTION = (
[ CONNECTION_NAME = '<connection-name>' ]
| [ ENDPOINT_URL = '<endpoint-url>' ]
[ ACCESS_KEY_ID = '<your-access-key-ID>' ]
[ SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = '<your-secret-access-key>' ]
[ ENABLE_VIRTUAL_HOST_STYLE = TRUE | FALSE ]
[ MASTER_KEY = '<your-master-key>' ]
[ REGION = '<region>' ]
[ SECURITY_TOKEN = '<security-token>' ]
[ ROLE_ARN = '<role-arn>' ]
[ EXTERNAL_ID = '<external-id>' ]
)
/* Azure Blob Storage */
| 'azblob://<container>[/<path>]'
CONNECTION = (
[ CONNECTION_NAME = '<connection-name>' ]
| ENDPOINT_URL = '<endpoint-url>'
ACCOUNT_NAME = '<account-name>'
ACCOUNT_KEY = '<account-key>'
)
/* Google Cloud Storage */
| 'gcs://<bucket>[/<path>]'
CONNECTION = (
[ CONNECTION_NAME = '<connection-name>' ]
| CREDENTIAL = '<your-base64-encoded-credential>'
)
/* Alibaba Cloud OSS */
| 'oss://<bucket>[/<path>]'
CONNECTION = (
[ CONNECTION_NAME = '<connection-name>' ]
| ACCESS_KEY_ID = '<your-ak>'
ACCESS_KEY_SECRET = '<your-sk>'
ENDPOINT_URL = '<endpoint-url>'
[ PRESIGN_ENDPOINT_URL = '<presign-endpoint-url>' ]
)
/* Tencent Cloud Object Storage */
| 'cos://<bucket>[/<path>]'
CONNECTION = (
[ CONNECTION_NAME = '<connection-name>' ]
| SECRET_ID = '<your-secret-id>'
SECRET_KEY = '<your-secret-key>'
ENDPOINT_URL = '<endpoint-url>'
)
/* Remote Files */
| 'https://<url>'
/* IPFS */
| 'ipfs://<your-ipfs-hash>'
CONNECTION = (ENDPOINT_URL = 'https://<your-ipfs-gateway>')
/* Hugging Face */
| 'hf://<repo-id>[/<path>]'
CONNECTION = (
[ REPO_TYPE = 'dataset' | 'model' ]
[ REVISION = '<revision>' ]
[ TOKEN = '<your-api-token>' ]
)
formatTypeOptions ::=
/* Common options for all formats */
[ COMPRESSION = AUTO | GZIP | BZ2 | BROTLI | ZSTD | DEFLATE | RAW_DEFLATE | XZ | NONE ]
/* CSV specific options */
[ RECORD_DELIMITER = '<character>' ]
[ FIELD_DELIMITER = '<character>' ]
[ SKIP_HEADER = <integer> ]
[ QUOTE = '<character>' ]
[ ESCAPE = '<character>' ]
[ NAN_DISPLAY = '<string>' ]
[ NULL_DISPLAY = '<string>' ]
[ ERROR_ON_COLUMN_COUNT_MISMATCH = TRUE | FALSE ]
[ EMPTY_FIELD_AS = null | string | field_default ]
[ BINARY_FORMAT = HEX | BASE64 ]
/* TSV specific options */
[ RECORD_DELIMITER = '<character>' ]
[ FIELD_DELIMITER = '<character>' ]
/* NDJSON specific options */
[ NULL_FIELD_AS = NULL | FIELD_DEFAULT ]
[ MISSING_FIELD_AS = ERROR | NULL | FIELD_DEFAULT ]
[ ALLOW_DUPLICATE_KEYS = TRUE | FALSE ]
/* PARQUET specific options */
[ MISSING_FIELD_AS = ERROR | FIELD_DEFAULT ]
/* ORC specific options */
[ MISSING_FIELD_AS = ERROR | FIELD_DEFAULT ]
/* AVRO specific options */
[ MISSING_FIELD_AS = ERROR | FIELD_DEFAULT ]
copyOptions ::=
[ SIZE_LIMIT = <num> ]
[ PURGE = <bool> ]
[ FORCE = <bool> ]
[ DISABLE_VARIANT_CHECK = <bool> ]
[ ON_ERROR = { continue | abort | abort_N } ]
[ MAX_FILES = <num> ]
[ RETURN_FAILED_ONLY = <bool> ]
[ COLUMN_MATCH_MODE = { case-sensitive | case-insensitive } ]
For remote files, you can use glob patterns to specify multiple files. For example:
ontime_200{6,7,8}.csvrepresentsontime_2006.csv,ontime_2007.csv,ontime_2008.csvontime_200[6-8].csvrepresents the same files
Key Parameters
-
FILES: Specifies one or more file names (separated by commas) to be loaded.
-
PATTERN: A PCRE2-based regular expression pattern string that specifies file names to match. See Example 4: Filtering Files with Pattern.
Format Type Options
The FILE_FORMAT parameter supports different file types, each with specific formatting options. Below are the available options for each supported file format:
- Common Options
- CSV
- TSV
- NDJSON
- PARQUET
- ORC
- AVRO
These options are available for all file formats:
| Option | Description | Values | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| COMPRESSION | Compression algorithm for data files | AUTO, GZIP, BZ2, BROTLI, ZSTD, DEFLATE, RAW_DEFLATE, XZ, NONE | AUTO |
| Option | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| RECORD_DELIMITER | Character(s) separating records | newline |
| FIELD_DELIMITER | Character(s) separating fields | comma (,) |
| SKIP_HEADER | Number of header lines to skip | 0 |
| QUOTE | Character used to quote fields | double-quote (") |
| ESCAPE | Escape character for enclosed fields | NONE |
| NAN_DISPLAY | String representing NaN values | NaN |
| NULL_DISPLAY | String representing NULL values | \N |
| ERROR_ON_COLUMN_COUNT_MISMATCH | Error if column count doesn't match | TRUE |
| EMPTY_FIELD_AS | How to handle empty fields | null |
| BINARY_FORMAT | Encoding format(HEX or BASE64) for binary data | HEX |
| Option | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| RECORD_DELIMITER | Character(s) separating records | newline |
| FIELD_DELIMITER | Character(s) separating fields | tab (\t) |
| Option | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| NULL_FIELD_AS | How to handle null fields | NULL |
| MISSING_FIELD_AS | How to handle missing fields | ERROR |
| ALLOW_DUPLICATE_KEYS | Allow duplicate object keys | FALSE |
| Option | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| MISSING_FIELD_AS | How to handle missing fields | ERROR |
| Option | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| MISSING_FIELD_AS | How to handle missing fields | ERROR |
| Option | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| MISSING_FIELD_AS | How to handle missing fields | ERROR |
Copy Options
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| SIZE_LIMIT | Maximum rows of data to load | 0 (no limit) |
| PURGE | Purges files after successful load | false |
| FORCE | Allows reloading of duplicate files | false (skips duplicates) |
| DISABLE_VARIANT_CHECK | Replaces invalid JSON with null | false (fails on invalid JSON) |
| ON_ERROR | How to handle errors: continue, abort, or abort_N | abort |
| MAX_FILES | Maximum number of files to load (up to 15,000) | - |
| RETURN_FAILED_ONLY | Only returns failed files in output | false |
| COLUMN_MATCH_MODE | For Parquet: column name matching mode | case-insensitive |
When importing large volumes of data, such as logs, it is recommended to set both PURGE and FORCE to true. This ensures efficient data import without the need for interaction with the Meta server (updating the copied-files set). However, it is important to be aware that this may lead to duplicate data imports.
Output
COPY INTO provides a summary of the data loading results with these columns:
| Column | Type | Nullable | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| FILE | VARCHAR | NO | The relative path to the source file. |
| ROWS_LOADED | INT | NO | The number of rows loaded from the source file. |
| ERRORS_SEEN | INT | NO | Number of error rows in the source file |
| FIRST_ERROR | VARCHAR | YES | The first error found in the source file. |
| FIRST_ERROR_LINE | INT | YES | Line number of the first error. |
If RETURN_FAILED_ONLY is set to true, the output will only contain the files that failed to load.
Examples
For external storage sources, it's recommended to use pre-created connections with the CONNECTION_NAME parameter instead of specifying credentials directly in the COPY statement. This approach provides better security, maintainability, and reusability. See CREATE CONNECTION for details on creating connections.
Example 1: Loading from Stages
These examples showcase data loading into Databend from various types of stages:
- User Stage
- Internal Stage
- External Stage
COPY INTO mytable
FROM @~
PATTERN = '.*[.]parquet'
FILE_FORMAT = (TYPE = PARQUET);
COPY INTO mytable
FROM @my_internal_stage
PATTERN = '.*[.]parquet'
FILE_FORMAT = (TYPE = PARQUET);
COPY INTO mytable
FROM @my_external_stage
PATTERN = '.*[.]parquet'
FILE_FORMAT = (TYPE = PARQUET);
Example 2: Loading from External Locations
These examples showcase data loading into Databend from various types of external sources:
- Amazon S3
- Azure Blob Storage
- Google Cloud Storage
- Remote Files
- IPFS
This example uses a pre-created connection to load data from Amazon S3:
-- First create a connection (you only need to do this once)
CREATE CONNECTION my_s3_conn
STORAGE_TYPE = 's3'
ACCESS_KEY_ID = '<your-access-key-ID>'
SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = '<your-secret-access-key>';
-- Use the connection to load data
COPY INTO mytable
FROM 's3://mybucket/data.csv'
CONNECTION = (CONNECTION_NAME = 'my_s3_conn')
FILE_FORMAT = (
TYPE = CSV,
FIELD_DELIMITER = ',',
RECORD_DELIMITER = '\n',
SKIP_HEADER = 1
)
SIZE_LIMIT = 10;
Using IAM Role (Recommended for Production)
-- Create connection using IAM role (more secure, recommended for production)
CREATE CONNECTION my_iam_conn
STORAGE_TYPE = 's3'
ROLE_ARN = 'arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/my_iam_role';
-- Load CSV files using the IAM role connection
COPY INTO mytable
FROM 's3://mybucket/'
CONNECTION = (CONNECTION_NAME = 'my_iam_conn')
PATTERN = '.*[.]csv'
FILE_FORMAT = (
TYPE = CSV,
FIELD_DELIMITER = ',',
RECORD_DELIMITER = '\n',
SKIP_HEADER = 1
);
This example connects to Azure Blob Storage and loads data from 'data.csv' into Databend:
-- Create connection for Azure Blob Storage
CREATE CONNECTION my_azure_conn
STORAGE_TYPE = 'azblob'
ENDPOINT_URL = 'https://<account_name>.blob.core.windows.net'
ACCOUNT_NAME = '<account_name>'
ACCOUNT_KEY = '<account_key>';
-- Use the connection to load data
COPY INTO mytable
FROM 'azblob://mybucket/data.csv'
CONNECTION = (CONNECTION_NAME = 'my_azure_conn')
FILE_FORMAT = (type = CSV);
This example connects to Google Cloud Storage and loads data:
-- Create connection for Google Cloud Storage
CREATE CONNECTION my_gcs_conn
STORAGE_TYPE = 'gcs'
CREDENTIAL = '<your-base64-encoded-credential>';
-- Use the connection to load data
COPY INTO mytable
FROM 'gcs://mybucket/data.csv'
CONNECTION = (CONNECTION_NAME = 'my_gcs_conn')
FILE_FORMAT = (
TYPE = CSV,
FIELD_DELIMITER = ',',
RECORD_DELIMITER = '\n',
SKIP_HEADER = 1
);
This example loads data from three remote CSV files and skips a file in case of errors.
COPY INTO mytable
FROM 'https://ci.databend.org/dataset/stateful/ontime_200{6,7,8}_200.csv'
FILE_FORMAT = (type = CSV)
ON_ERROR = continue;
This example loads data from a CSV file on IPFS:
COPY INTO mytable
FROM 'ipfs://<your-ipfs-hash>'
CONNECTION = (
ENDPOINT_URL = 'https://<your-ipfs-gateway>'
)
FILE_FORMAT = (
TYPE = CSV,
FIELD_DELIMITER = ',',
RECORD_DELIMITER = '\n',
SKIP_HEADER = 1
);
Example 3: Loading Compressed Data
This example loads a GZIP-compressed CSV file on Amazon S3 into Databend:
-- Create connection for compressed data loading
CREATE CONNECTION compressed_s3_conn
STORAGE_TYPE = 's3'
ACCESS_KEY_ID = '<your-access-key-ID>'
SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = '<your-secret-access-key>';
-- Load GZIP-compressed CSV file using the connection
COPY INTO mytable
FROM 's3://mybucket/data.csv.gz'
CONNECTION = (CONNECTION_NAME = 'compressed_s3_conn')
FILE_FORMAT = (
TYPE = CSV,
FIELD_DELIMITER = ',',
RECORD_DELIMITER = '\n',
SKIP_HEADER = 1,
COMPRESSION = AUTO
);
Example 4: Filtering Files with Pattern
This example demonstrates how to load CSV files from Amazon S3 using pattern matching with the PATTERN parameter. It filters files with 'sales' in their names and '.csv' extensions:
-- Create connection for pattern-based file loading
CREATE CONNECTION pattern_s3_conn
STORAGE_TYPE = 's3'
ACCESS_KEY_ID = '<your-access-key-ID>'
SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = '<your-secret-access-key>';
-- Load CSV files with 'sales' in their names using pattern matching
COPY INTO mytable
FROM 's3://mybucket/'
CONNECTION = (CONNECTION_NAME = 'pattern_s3_conn')
PATTERN = '.*sales.*[.]csv'
FILE_FORMAT = (
TYPE = CSV,
FIELD_DELIMITER = ',',
RECORD_DELIMITER = '\n',
SKIP_HEADER = 1
);
Where .* is interpreted as zero or more occurrences of any character. The square brackets escape the period character . that precedes a file extension.
To load from all the CSV files using a connection:
COPY INTO mytable
FROM 's3://mybucket/'
CONNECTION = (CONNECTION_NAME = 'pattern_s3_conn')
PATTERN = '.*[.]csv'
FILE_FORMAT = (
TYPE = CSV,
FIELD_DELIMITER = ',',
RECORD_DELIMITER = '\n',
SKIP_HEADER = 1
);
When specifying the pattern for a file path including multiple folders, consider your matching criteria:
- If you want to match a specific subpath following a prefix, include the prefix in the pattern (e.g., 'multi_page/') and then specify the pattern you want to match within that subpath (e.g., '_page_1').
-- File path: parquet/multi_page/multi_page_1.parquet
COPY INTO ... FROM @data/parquet/ PATTERN = 'multi_page/.*_page_1.*') ...
- If you want to match any part of the file path that contains the desired pattern, use '.*' before and after the pattern (e.g., '.*multi_page_1.*') to match any occurrences of 'multi_page_1' within the path.
-- File path: parquet/multi_page/multi_page_1.parquet
COPY INTO ... FROM @data/parquet/ PATTERN ='.*multi_page_1.*') ...
Example 5: Loading to Table with Extra Columns
This section demonstrates data loading into a table with extra columns, using the sample file books.csv:
Transaction Processing,Jim Gray,1992
Readings in Database Systems,Michael Stonebraker,2004
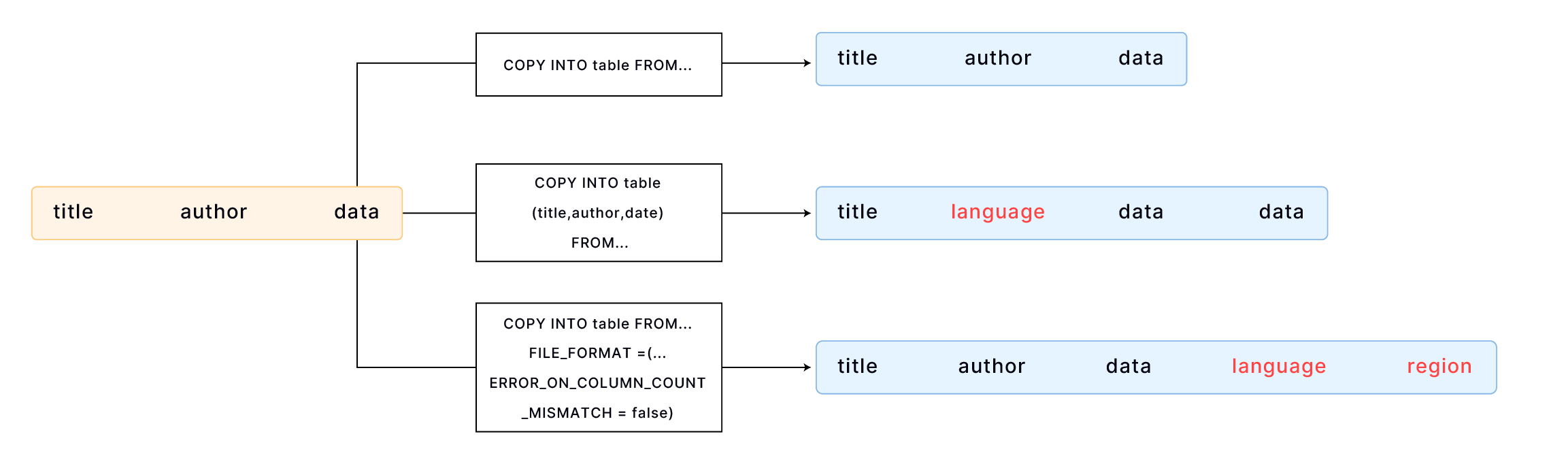
By default, COPY INTO loads data into a table by matching the order of fields in the file to the corresponding columns in the table. It's essential to ensure that the data aligns correctly between the file and the table. For example,
CREATE TABLE books
(
title VARCHAR,
author VARCHAR,
date VARCHAR
);
COPY INTO books
FROM 'https://datafuse-1253727613.cos.ap-hongkong.myqcloud.com/data/books.csv'
FILE_FORMAT = (TYPE = CSV);
If your table has more columns than the file, you can specify the columns into which you want to load data. For example,
CREATE TABLE books_with_language
(
title VARCHAR,
language VARCHAR,
author VARCHAR,
date VARCHAR
);
COPY INTO books_with_language (title, author, date)
FROM 'https://datafuse-1253727613.cos.ap-hongkong.myqcloud.com/data/books.csv'
FILE_FORMAT = (TYPE = CSV);
If your table has more columns than the file, and the additional columns are at the end of the table, you can load data using the FILE_FORMAT option ERROR_ON_COLUMN_COUNT_MISMATCH. This allows you to load data without specifying each column individually. Please note that ERROR_ON_COLUMN_COUNT_MISMATCH currently works for the CSV file format.
CREATE TABLE books_with_extra_columns
(
title VARCHAR,
author VARCHAR,
date VARCHAR,
language VARCHAR,
region VARCHAR
);
COPY INTO books_with_extra_columns
FROM 'https://datafuse-1253727613.cos.ap-hongkong.myqcloud.com/data/books.csv'
FILE_FORMAT = (TYPE = CSV, ERROR_ON_COLUMN_COUNT_MISMATCH = false);
Extra columns in a table can have default values specified by CREATE TABLE or ALTER TABLE. If a default value is not explicitly set for an extra column, the default value associated with its data type will be applied. For instance, an integer-type column will default to 0 if no other value is specified.
Example 6: Loading JSON with Custom Format
This example loads data from a CSV file "data.csv" with the following content:
1,"U00010","{\"carPriceList\":[{\"carTypeId":10,\"distance":5860},{\"carTypeId":11,\"distance\":5861}]}"
2,"U00011","{\"carPriceList\":[{\"carTypeId":12,\"distance":5862},{\"carTypeId":13,\"distance\":5863}]}"
Each line contains three columns of data, with the third column being a string containing JSON data. To load CSV data correctly with JSON fields, we need to set the correct escape character. This example uses the backslash \ as the escape character, as the JSON data contains double quotes ".
Step 1: Create custom file format.
-- Define a custom CSV file format with the escape character set to backslash \
CREATE FILE FORMAT my_csv_format
TYPE = CSV
ESCAPE = '\\';
Step 2: Create target table.
CREATE TABLE t
(
id INT,
seq VARCHAR,
p_detail VARCHAR
);
Step 3: Load with custom file format.
COPY INTO t FROM @t_stage FILES=('data.csv')
FILE_FORMAT=(FORMAT_NAME='my_csv_format');
Example 7: Loading Invalid JSON
When loading data into a Variant column, Databend automatically checks the data's validity and throws an error in case of any invalid data. For example, if you have a Parquet file named invalid_json_string.parquet in the user stage that contains invalid JSON data, like this:
SELECT *
FROM @~/invalid_json_string.parquet;
┌────────────────────────────────────┐
│ a │ b │
├─────────────────┼──────────────────┤
│ 5 │ {"k":"v"} │
│ 6 │ [1, │
└────────────────────────────────────┘
DESC t2;
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Field │ Type │ Null │ Default │ Extra │
├────────┼─────────┼────────┼─────────┼────────┤
│ a │ VARCHAR │ YES │ NULL │ │
│ b │ VARIANT │ YES │ NULL │ │
└──────────────────────────────────────────────┘
An error would occur when attempting to load the data into a table:
COPY INTO t2 FROM @~/invalid_json_string.parquet FILE_FORMAT = (TYPE = PARQUET) ON_ERROR = CONTINUE;
error: APIError: ResponseError with 1006: EOF while parsing a value, pos 3 while evaluating function `parse_json('[1,')`
To load without checking the JSON validity, set the option DISABLE_VARIANT_CHECK to true in the COPY INTO statement:
COPY INTO t2 FROM @~/invalid_json_string.parquet
FILE_FORMAT = (TYPE = PARQUET)
DISABLE_VARIANT_CHECK = true
ON_ERROR = CONTINUE;
┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ File │ Rows_loaded │ Errors_seen │ First_error │ First_error_line │
├─────────────────────────────┼─────────────┼─────────────┼──────────────────┼──────────────────┤
│ invalid_json_string.parquet │ 2 │ 0 │ NULL │ NULL │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
SELECT * FROM t2;
-- Invalid JSON is stored as null in the Variant column.
┌──────────────────────────────────────┐
│ a │ b │
├──────────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ 5 │ {"k":"v"} │
│ 6 │ null │
└──────────────────────────────────────┘