Access Control
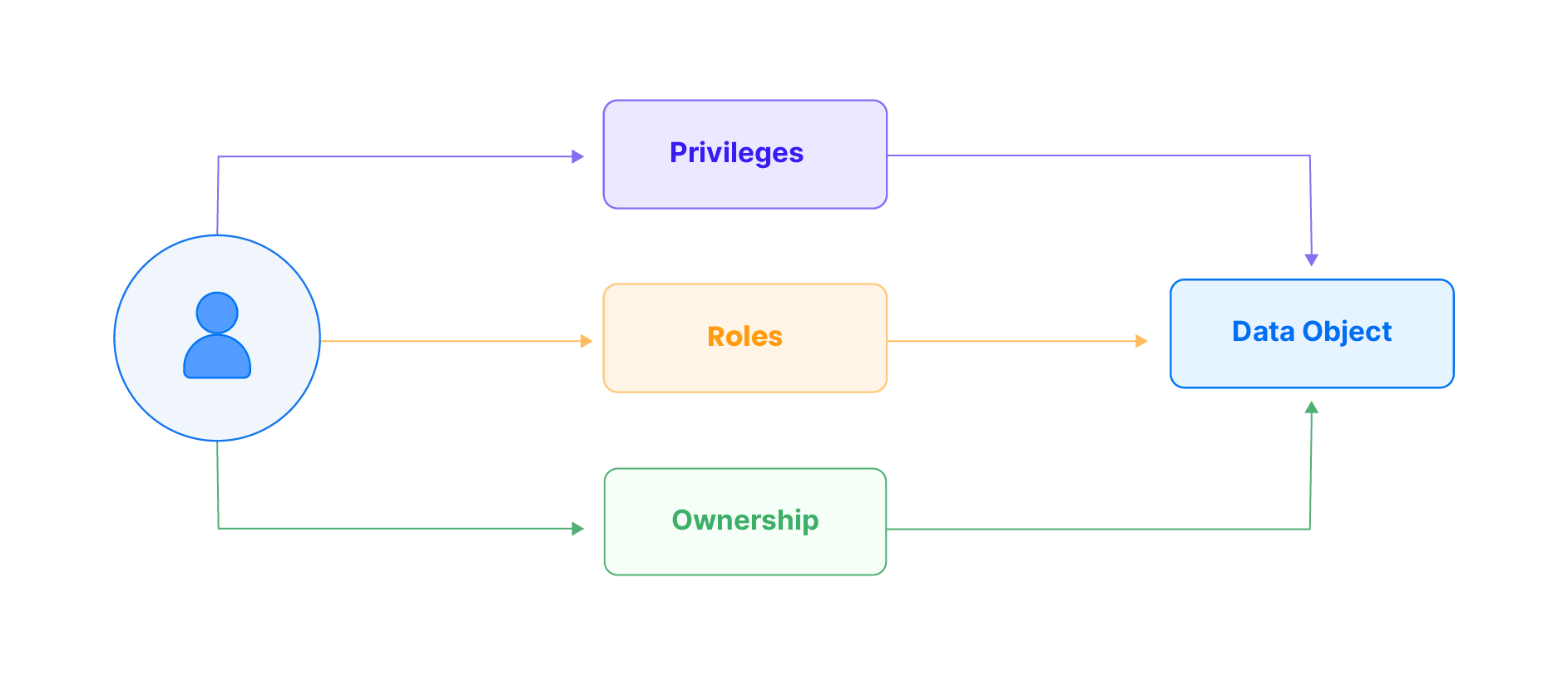
Databend incorporates both Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Discretionary Access Control (DAC) models for its access control functionality. When a user accesses a data object in Databend, they must be granted appropriate privileges or roles, or they need to have ownership of the data object. A data object can refer to various elements, such as a database, table, view, stage, or UDF.
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Privileges | Privileges play a crucial role when interacting with data objects in Databend. These permissions, such as read, write, and execute, provide precise control over user actions, ensuring alignment with user requirements and maintaining data security. |
| Roles | Roles simplify access control. Roles are predefined sets of privileges assigned to users, streamlining permission management. Administrators can categorize users based on responsibilities, granting permissions efficiently without individual configurations. |
| Ownership | Ownership is a specialized privilege for controlling data access. When a user owns a data object, they have the highest control level, dictating access permissions. This straightforward ownership model empowers users to manage their data, controlling who can access or modify it within the Databend environment. |
This guide describes the related concepts and provides instructions on how to manage access control in Databend: