Virtual Column: Automatic Acceleration for JSON Data
Virtual columns automatically accelerate queries on semi-structured data stored in VARIANT columns. This feature provides zero-configuration performance optimization for JSON data access.
What Problem Does It Solve?
When querying JSON data, traditional databases must parse the entire JSON structure every time you access a nested field. This creates performance bottlenecks:
| Problem | Impact | Virtual Column Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Query Latency | Complex JSON queries take seconds | Sub-second response times |
| Excessive Data Reading | Must read entire JSON documents even for single fields | Read only the specific fields needed |
| Slow JSON Parsing | Every query re-parses entire JSON documents | Pre-materialized fields for instant access |
| High CPU Usage | JSON traversal consumes processing power | Direct column reads like regular data |
| Memory Overhead | Loading full JSON structures into memory | Only load needed fields |
Example Scenario: An e-commerce analytics table with product data in JSON format. Without virtual columns, querying product_data['category'] across millions of rows requires parsing every JSON document. With virtual columns, it becomes a direct column lookup.
How It Works Automatically
- Data Ingestion → Databend analyzes JSON structure in VARIANT columns
- Smart Detection → System identifies frequently accessed nested fields
- Background Optimization → Virtual columns are created automatically
- Query Acceleration → Queries automatically use optimized paths
Configuration
Virtual columns are enabled by default starting from v1.2.832 and require no additional configuration.
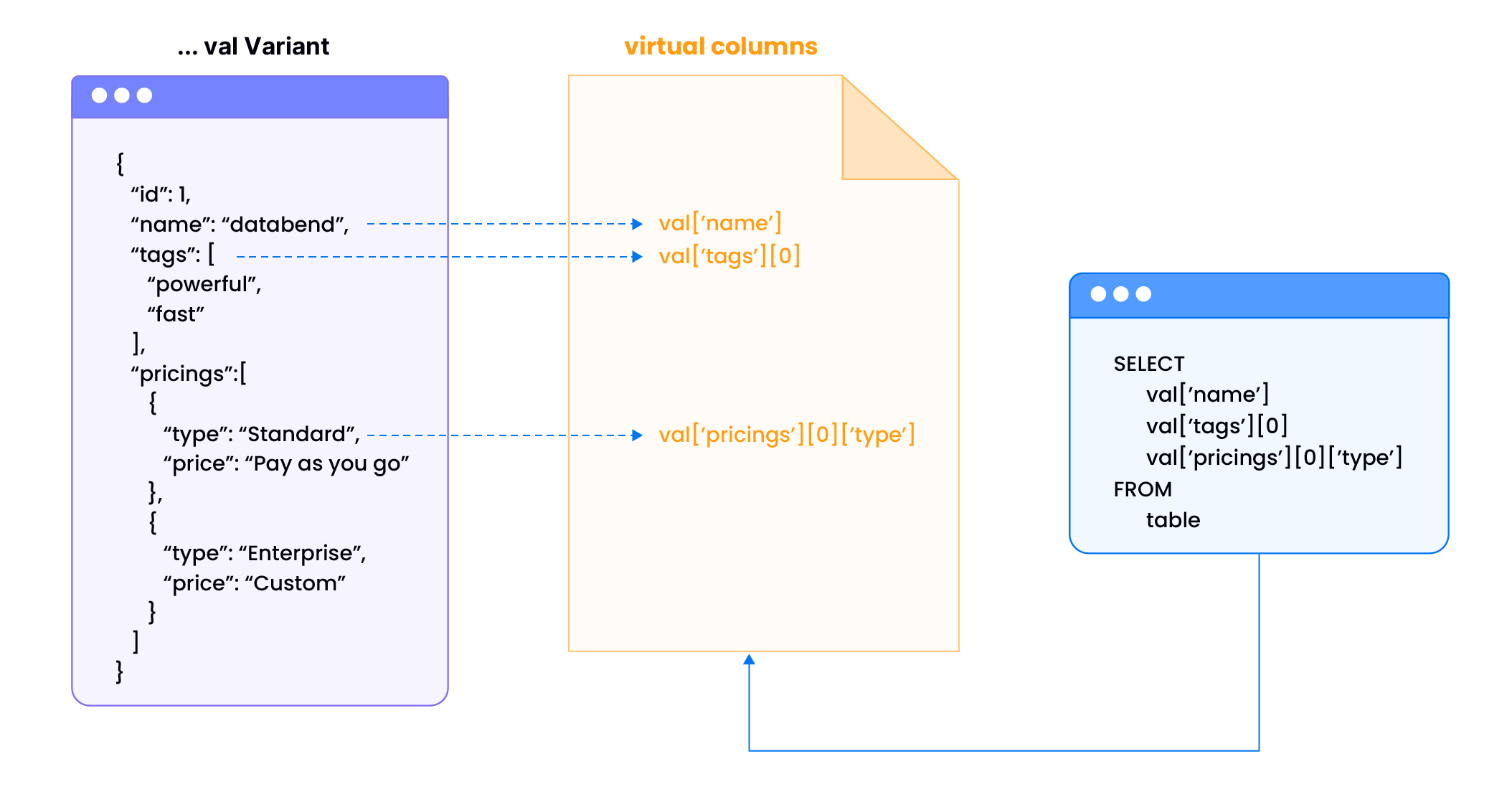
Complete Example
This example demonstrates automatic virtual column creation and performance benefits:
-- Create a table named 'test' with columns 'id' and 'val' of type Variant.
CREATE TABLE test(id int, val variant);
-- Insert sample records into the 'test' table with Variant data.
INSERT INTO
test
VALUES
(
1,
'{"id":1,"name":"databend","tags":["powerful","fast"],"pricings":[{"type":"Standard","price":"Pay as you go"},{"type":"Enterprise","price":"Custom"}]}'
),
(
2,
'{"id":2,"name":"databricks","tags":["scalable","flexible"],"pricings":[{"type":"Free","price":"Trial"},{"type":"Premium","price":"Subscription"}]}'
),
(
3,
'{"id":3,"name":"snowflake","tags":["cloud-native","secure"],"pricings":[{"type":"Basic","price":"Pay per second"},{"type":"Enterprise","price":"Annual"}]}'
),
(
4,
'{"id":4,"name":"redshift","tags":["reliable","scalable"],"pricings":[{"type":"On-Demand","price":"Pay per usage"},{"type":"Reserved","price":"1 year contract"}]}'
),
(
5,
'{"id":5,"name":"bigquery","tags":["innovative","cost-efficient"],"pricings":[{"type":"Flat Rate","price":"Monthly"},{"type":"Flex","price":"Per query"}]}'
);
INSERT INTO test SELECT * FROM test;
INSERT INTO test SELECT * FROM test;
INSERT INTO test SELECT * FROM test;
INSERT INTO test SELECT * FROM test;
INSERT INTO test SELECT * FROM test;
-- Explain the query execution plan for selecting specific fields from the table.
EXPLAIN
SELECT
val ['name'],
val ['tags'] [0],
val ['pricings'] [0] ['type']
FROM
test;
-[ EXPLAIN ]-----------------------------------
Exchange
├── output columns: [test.val['name'] (#3), test.val['pricings'][0]['type'] (#5), test.val['tags'][0] (#8)]
├── exchange type: Merge
└── TableScan
├── table: default.default.test
├── output columns: [val['name'] (#3), val['pricings'][0]['type'] (#5), val['tags'][0] (#8)]
├── read rows: 160
├── read size: 1.69 KiB
├── partitions total: 6
├── partitions scanned: 6
├── pruning stats: [segments: <range pruning: 6 to 6>, blocks: <range pruning: 6 to 6>]
├── push downs: [filters: [], limit: NONE]
├── virtual columns: [val['name'], val['pricings'][0]['type'], val['tags'][0]]
└── estimated rows: 160.00
-- Explain the query execution plan for selecting only the 'name' field from the table.
EXPLAIN
SELECT
val ['name']
FROM
test;
-[ EXPLAIN ]-----------------------------------
Exchange
├── output columns: [test.val['name'] (#2)]
├── exchange type: Merge
└── TableScan
├── table: default.book_db.test
├── output columns: [val['name'] (#2)]
├── read rows: 160
├── read size: < 1 KiB
├── partitions total: 16
├── partitions scanned: 16
├── pruning stats: [segments: <range pruning: 6 to 6>, blocks: <range pruning: 16 to 16>]
├── push downs: [filters: [], limit: NONE]
├── virtual columns: [val['name']]
└── estimated rows: 160.00
-- Display all the auto generated virtual columns.
SHOW VIRTUAL COLUMNS WHERE table='test';
╭────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ database │ table │ source_column │ virtual_column_id │ virtual_column_name │ virtual_column_type │
│ String │ String │ String │ UInt32 │ String │ String │
├──────────┼────────┼───────────────┼───────────────────┼──────────────────────────┼─────────────────────┤
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000000 │ ['id'] │ UInt64 │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000001 │ ['name'] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000002 │ ['pricings'][0]['price'] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000003 │ ['pricings'][0]['type'] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000004 │ ['pricings'][1]['price'] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000005 │ ['pricings'][1]['type'] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000006 │ ['tags'][0] │ String │
│ default │ test │ val │ 3000000007 │ ['tags'][1] │ String │
╰────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
Monitoring Commands
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
SHOW VIRTUAL COLUMNS | View automatically created virtual columns |
REFRESH VIRTUAL COLUMN | Manually refresh virtual columns |
FUSE_VIRTUAL_COLUMN | View virtual column metadata |
Performance Results
Virtual columns typically provide:
- 5-10x faster JSON field access
- Automatic optimization without query changes
- Reduced resource consumption during query processing
- Transparent acceleration for existing applications
Virtual columns work automatically in the background—Databend optimizes your JSON queries with zero configuration.