Automating Data Loading with Tasks
Tasks wrap SQL so Databend can run it for you on a schedule or when a condition is met. Keep the following knobs in mind when you define one with CREATE TASK:
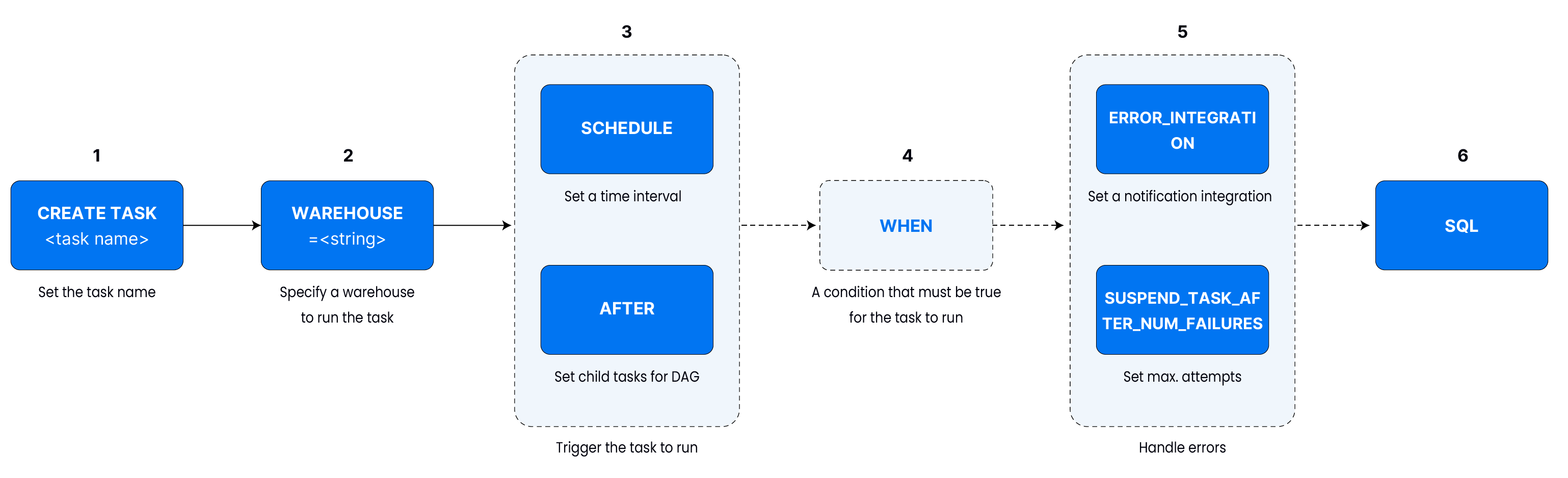
- Name & warehouse – every task needs a warehouse.
CREATE TASK ingest_orders
WAREHOUSE = 'etl_wh'
AS SELECT 1; - Trigger – fixed interval, CRON, or
AFTER another_task.CREATE TASK mytask
WAREHOUSE = 'default'
SCHEDULE = 2 MINUTE
AS ...; - Guards – only run when a predicate is true.
CREATE TASK mytask
WAREHOUSE = 'default'
WHEN STREAM_STATUS('mystream') = TRUE
AS ...; - Error handling – pause after N failures or send notifications.
CREATE TASK mytask
WAREHOUSE = 'default'
SUSPEND_TASK_AFTER_NUM_FAILURES = 3
AS ...; - SQL payload – whatever you place after
ASis what the task executes.CREATE TASK bump_age
WAREHOUSE = 'default'
SCHEDULE = USING CRON '0 0 1 1 * *' 'UTC'
AS UPDATE employees SET age = age + 1;
Example 1: Scheduled Copy
Continuously generate sensor data, land it as Parquet, and load it into a table. Replace 'etl_wh_small' with your warehouse name in every CREATE/ALTER TASK statement.
Step 1. Prepare demo objects
-- Create a playground schema and target table
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS task_demo;
USE task_demo;
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE sensor_events (
event_time TIMESTAMP,
sensor_id INT,
temperature DOUBLE,
humidity DOUBLE
);
-- Stage that will store the generated Parquet files
CREATE OR REPLACE STAGE sensor_events_stage;
Step 2. Task 1 — Generate files
task_generate_data writes 100 random readings to the stage once per minute. Each execution produces a fresh Parquet file that downstream consumers can ingest.
CREATE OR REPLACE TASK task_generate_data
WAREHOUSE = 'etl_wh_small' -- replace with your warehouse
SCHEDULE = 1 MINUTE
AS
COPY INTO @sensor_events_stage
FROM (
SELECT
NOW() AS event_time,
number AS sensor_id,
20 + RAND() * 5 AS temperature,
60 + RAND() * 10 AS humidity
FROM numbers(100)
)
FILE_FORMAT = (TYPE = PARQUET);
Step 3. Task 2 — Load the files
task_consume_data scans the stage on the same cadence and copies every newly generated Parquet file into the sensor_events table. The PURGE = TRUE clause cleans up files that were already ingested.
CREATE OR REPLACE TASK task_consume_data
WAREHOUSE = 'etl_wh_small' -- replace with your warehouse
SCHEDULE = 1 MINUTE
AS
COPY INTO sensor_events
FROM @sensor_events_stage
PATTERN = '.*[.]parquet'
FILE_FORMAT = (TYPE = PARQUET)
PURGE = TRUE;
Step 4. Resume tasks
ALTER TASK task_generate_data RESUME;
ALTER TASK task_consume_data RESUME;
Both tasks start in a suspended state until you resume them. Expect the first files and copies to happen within the next minute.
Step 5. Monitor the pipeline
-- Confirm that the tasks are running
SHOW TASKS LIKE 'task_%';
-- Inspect files on the stage (should shrink as PURGE removes processed files)
LIST @sensor_events_stage;
-- Check the ingested rows
SELECT *
FROM sensor_events
ORDER BY event_time DESC
LIMIT 5;
-- Review recent executions for troubleshooting
SELECT *
FROM task_history('task_consume_data', 5);
-- Change configuration later if needed
ALTER TASK task_consume_data
SCHEDULE = 30 SECOND,
WAREHOUSE = 'etl_wh_medium'; -- replace with your warehouse
You can suspend either task with ALTER TASK ... SUSPEND when you finish testing.
Step 6. Update tasks
You can change schedules, warehouses, or even the SQL payload without dropping the task:
-- Tweak the schedule and warehouse
ALTER TASK task_consume_data
SCHEDULE = 30 SECOND,
WAREHOUSE = 'etl_wh_medium'; -- replace with your warehouse
-- Update the SQL payload (replace the existing body)
ALTER TASK task_consume_data
AS
COPY INTO sensor_events
FROM @sensor_events_stage
FILE_FORMAT = (TYPE = PARQUET);
-- Resume after edits (tasks suspend when their SQL changes)
ALTER TASK task_consume_data RESUME;
-- Review execution history for verification
SELECT *
FROM task_history('task_consume_data', 5)
ORDER BY completed_time DESC;
TASK_HISTORY returns status, timing, and query IDs, making it easy to double-check changes.
Example 2: Stream-Triggered Merge
Use WHEN STREAM_STATUS(...) to fire only when a stream has new rows. Reuse the sensor_events table from Example 1.
Step 1. Create stream + latest table
-- Create a stream on the sensor table (Standard mode to capture every mutation)
CREATE OR REPLACE STREAM sensor_events_stream
ON TABLE sensor_events
APPEND_ONLY = false;
-- Target table that keeps only the latest copy of each row
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE sensor_events_latest AS
SELECT *
FROM sensor_events
WHERE 1 = 0;
Step 2. Create the conditional task
CREATE OR REPLACE TASK task_stream_merge
WAREHOUSE = 'etl_wh_small' -- replace with your warehouse
SCHEDULE = 1 MINUTE
WHEN STREAM_STATUS('task_demo.sensor_events_stream') = TRUE
AS
INSERT INTO sensor_events_latest
SELECT *
FROM sensor_events_stream;
ALTER TASK task_stream_merge RESUME;
Step 3. Verify the behavior
SELECT *
FROM sensor_events_latest
ORDER BY event_time DESC
LIMIT 5;
SELECT *
FROM task_history('task_stream_merge', 5);
The task fires only when STREAM_STATUS('<database>.<stream_name>') returns TRUE. Always prefix the stream with its database (for example task_demo.sensor_events_stream) so the task can resolve it regardless of the current schema, and use your own warehouse name in every CREATE/ALTER TASK.